News&Topics
FPP RESEARCH FORUM - Potential Benefits of Fermented Papaya Preparation in Humans Health Following Exposure to Radiation -
The Osato Research Institute (O.R.I.) has been focusing on the effect of radiation to the human body during airline travels and addressing the question as the possible protection that fermented papaya preparation could have towards radiation-induced biological damage through basic research and clinical trials. During a typical 13- hour flight from Tokyo to New York for example, passengers and the airline crew are likely to be exposed to 100μSv of natural cosmic radiation which is equivalent to approximately 7.7μSv/hour (Figure 1). However, it is safe to travel by airplane and the risk of radiation exposure during flights has not been proven scientifically. Nevertheless, a healthy person on a long flight with adequate antioxidant and immune function integrity can have increased protection against the aviation radiation exposure. In the case of compromised health status where the immune system might be weakened, oxidative DNA damage due to the radiation exposure might take longer to repair due to compromised repair mechanisms. Similarly the effect on the individual's homeostasis might mean that returning to normal physiological state might take longer, thus increasing the risk of inflammatory reactions.
Since the occurrence of the FUKUSHIMA Nuclear Power Plant accident, due to the greatest earthquake and tsunami in that has ever been experienced in Japan, the effect that radioactivity has on body has been drawing a lot of attention around the world. The environmental radioactivity level in Tokyo was 0.8μSv/h just after the Fukushima hydrogen explosion on March 15th in Tokyo. This is about one-tenth of the aforementioned radiation dose received during a long flight and recorded only temporarily. Although this figure came back normal to 0.028~0.079μSv/h and the average of April 21th is 0.072μSv/h, many people remained anxious about the harzards presented by the potential exposure.
Therefore, we decided to transmit an emergency message regarding the effect of radiation to the human body and the effectiveness of FPP against the damage.
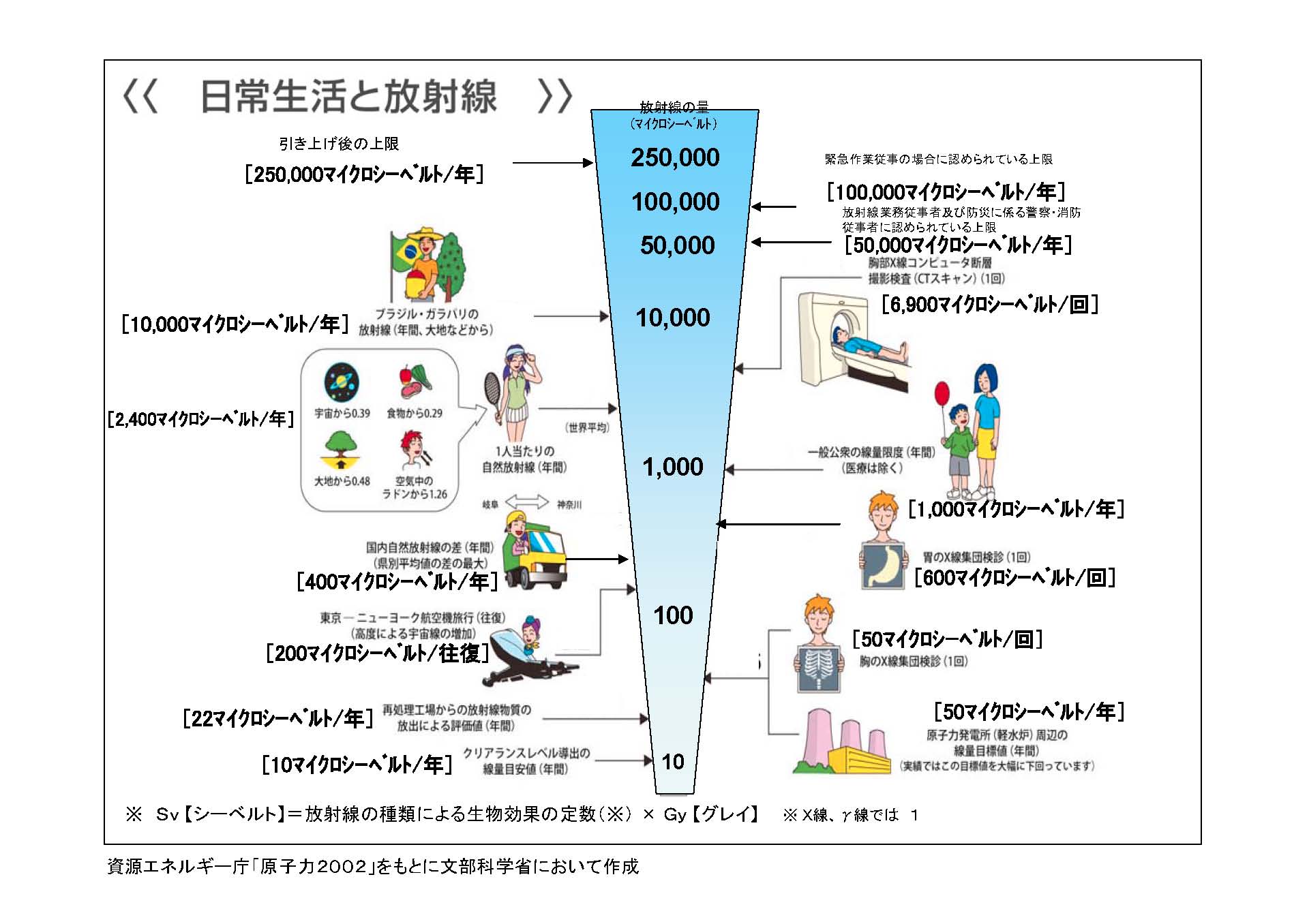 Figure 1. : Reported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology - JAPAN
The maximum reading of the environmental radioactivity level in Tokyo was 0.8μSv/h (3.15. 2011)
Figure 1. : Reported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology - JAPAN
The maximum reading of the environmental radioactivity level in Tokyo was 0.8μSv/h (3.15. 2011)
The action pathway of radiation to the human body can visualized in two ways: one is direct action and the other one is an indirect action. (Figure 2) The direct action is DNA breakage. DNA has essential information to make body. The damaged DNA would cause apoptosis and mutation of cells and increase a risk of diseases. (Figure 3) The indirect action is generation of radical oxygen in the human body. We are influenced by radiation not only through environment exposure but also through breathing air and eating food. The DNA base damage mediated by radical oxygen would disturb normal cell growth and cause a functional decline of the body.
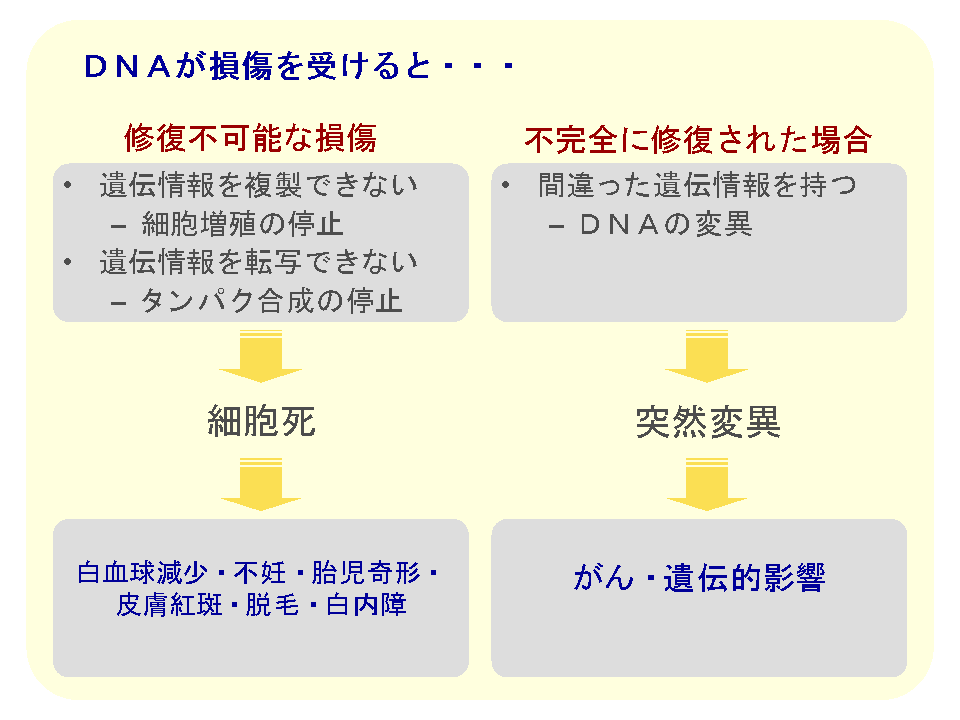 Figure 2. : Action Pathways of radiation to the human body on DNA
Figure 2. : Action Pathways of radiation to the human body on DNA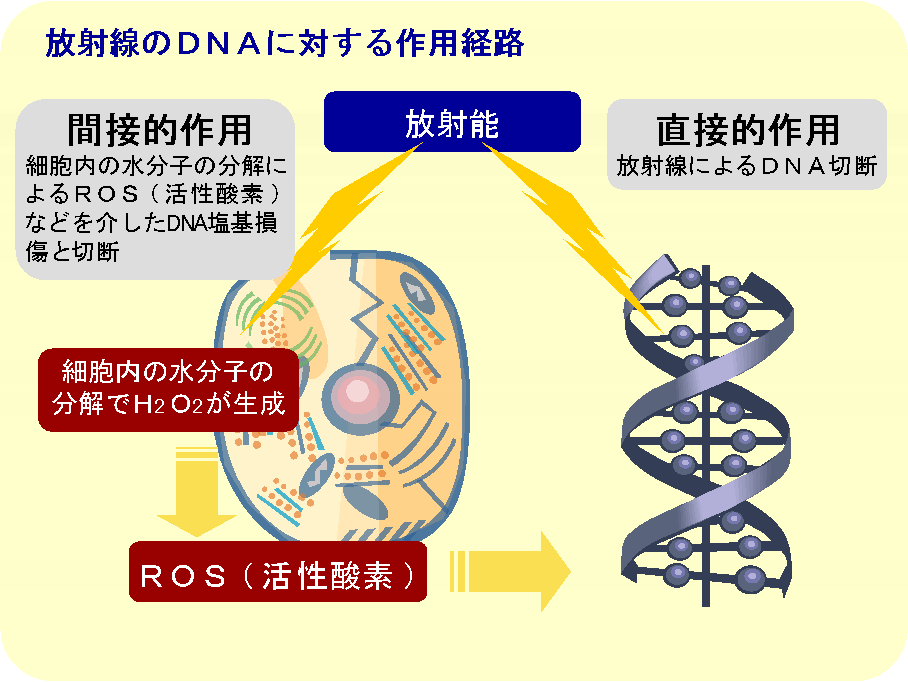 Figure 3. : Influence of DNA damage
Figure 3. : Influence of DNA damageFPP adjust the functions of anti-oxidant systems and immune systems and many papers on the clinical trials have been presented. FPP can prevent DNA damage and inflammation as well as reduce the risk for developing diseases and helps the quick recovery of damaged tissues in the human body.
Normal cellular metabolism is widely acknowledged as the source of endogenous reactive oxygen species (ROS), and it is these cellular processes that are largely responsible for the background levels of oxidative DNA damage detected in normal tissue. ROS may also be generated by ionizing or ultraviolet radiation. Equally, certain exogenous chemicals may redox cycle following metabolism by the cell, with the subsequent production of electrons that can be transferred to molecular oxygen producing the superoxide anion (a free radical denoted as O2•-). Dismutation of the superoxide anion generates the hydrogen peroxide inside the cells and tissues and these together with the complex interaction with other ROS (such as the reactive hydroxyl radical) can damage cellular biomolecules, such as DNA, leading to modification and potentially serious consequences for the cell if the DNA damage is not repaired. One such DNA oxidation product is 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OH-dG). It is most notable that FPP consumption reduces 8-OHdG levels and this is an important biomarker outcome for DNA damage, and controls DNA adduct, which may impact the progression towards the development of cancer. FPP consumption is associated with gene expression of SOD (an enzyme responsible for the elimination of the superoxide anion), as well as hOGG1 (a DNA repair enzyme responsible for the elimination of 8-OHdG from oxidative DNA). That both enzymes are involved with biological repair and defense system of our own body, suggests that FPP has functions that are highly beneficial to human health.
Further, FPP has potential to reduce the risk of developing disease due to oxidative DNA damage.Research at ORI will continue to define the potential defense function of FPP against radiation induced physiological changes as in chronic human diseases.
- FPP Papers on DNA damage and Anti-oxidation -
Click the titles of the papers, and a new window will open to read the summary.◆Anti-oxidant effect
1). Nutraceutical Supplementation: Effect of a Fermented Papaya Preparation on Redox Status and DNA Damage in Healthy Elderly Individuals and Relationship with GSTM1 Genotype
F. MAROTTA, M. WEKSLER, Y. NAITO, C. YOSHIDA, M. YOSHIOKA, AND P. MARANDOLA,
Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1067, 400-407 (2006)
The study was conducted on 54 elderly patients without major invalidating diseases for 3 months. The fermented papaya preparation (FPP)-supplemented group showed a decrease in 8-OHdG, which is a marker of lymphocyte DNA damage, and improvement in DNA adduct, which is a marker of cancer-causing risk. Especially a subgroup without GSTM1 gene, under FPP treatment, showed a significant decrease in 8-OHdG and DNA adduct.
2). Oxidative-inflammatory damage in cirrhosis: Effect of vitamin E and a fermented papaya preparation
Francesco Marotta, Chisato Yoshida, R Barreto, Yasuhiro Naito, E Fesce and Lester Packer,
J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 22, 697-703 (2007)
The study was conducted on 50 patients with HCV-related cirrhosis for 6 months. The fermented papaya preparation (FPP)-supplemented group showed improvement in GSH、GPx、GSSG、MDA、serum TNF-α、lymphocyte 8-OHdG and became close to the concentration level of a healthy person. Cirrhosis patients would develop liver cancer with continuous oxidative stress. The present data seem to suggest a potential supportive role of antioxidants/immunomodulators as FPP in cirrhosis patients.
3). Assessment of the effect of fermented papaya preparation on oxidative damage in spontaneously hypertensive rat brain using electron spin resonance (ESR) imaging and L-band ESR spectroscopy
Fumihiko Yoshino, Masaichi-Chang-il Lee, Kyo Kobayashi, Yuki Hayashi, Okezie I. Aruoma,
Journal of Functional Foods 1 , 375-380 (2009)
We measured free radicals in spontaneously hypertensive rat brain by using electron spin resonance (ESR) imaging and L-band ESR spectroscopy and got a result that FPP-supplemented rats showed quicker elimination of free radicals.
4). Amelioration of Oxidative Stress in Red Blood Cells from Patients with β-thalassemia Major and Intermedia and E-β-thalassemia Following Administration of a Fermented Papaya Preparation
Eitan Fibach, Ee-Shien Tan, Saumya Jamuar, Ivy Ng, Johnny Amer and Eliezer A. Rachmilewitz,
Phytother. Res. 24, 1334-1338 (2010)
The study was conducted on β-thalassemia patients, who have genetic defects in blood, for 6 months. FPP treatment increased the content of reduced glutathione (GSH) in red blood cells (RBC), and decreased their reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. We got the same results in the clinical trials in Israel, Singapore and Thai as well. It seems to suggest that FPP improves the oxidative states in the diseases mediated by oxidative stress such as thalassemia.
◆Anti-inflammatory effect
1). Nutraceutical Strategy in Aging Targeting Heat Shock Protein and Inflammatory Profile through Understanding Interleukin-6 Polymorphism
F. MAROTTA, K. KOIKE, A. LORENZETTI, Y. NAITO, F. FAYET, H. SHIMIZU, AND P. MARANDOLA,
Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1119, 196-202 (2007)
The study was conducted on 40 elderly, generally healthy subjects for 3 months. FPP treatment normalized the inflammatory parameters with a decrease of inflammatory markers such as IL-6 and TNF-α and a rise of protective Heat Shock Protein such as Hsp70.
2). Improved Function of Diabetic Wound-Site Macrophages and Accelerated Wound Closure in Response to Oral Supplementation of a Fermented Papaya Preparation
Eric Collard and Sashwati Roy,
Antioxid. Redox Signal. 13, 599-606 (2010)
Eight weeks of oral FPP supplementation to diabetic(db/db) mice resulted in attenuation in the gain of blood glucose without any effects on body weight gain, including lower LDL, TGL and Total cholesterol levels and an increase in HDL levels. FPP-supplemented mice showed a significant increase in the rate of wound closure and wound angiogenesis. Also, the iNOS and VEGF gene expression were markedly upregulated in the wounds. These results suggest that FPP could activate the macrophage function which is associated with wound closure and accelerate time to recover from the wound.
◆Gene Expression
1). Regulating Redox Balance Gene Expression in Healthy Individuals by Nutraceuticals: A Pilot Study
Francesco Marotta, Keiko Koike, Aldo Lorenzetti, Shalini Jain, Paola Signorelli, Yussef Metugriachuk, Pierre Mantello, and Nicola Locorotondo,
Rejuvenat Res. 13, 175-178 (2010)
The study was conducted on 11 healthy, nonsmoking, teetotaler individuals who do not take any vitamins or supplements for 4 weeks. The redox status was assessed by expression level of genes which produce GPx、SOD、hOGG1. At 2-week observation, FPP brought about a significant upregulation of all gene expressions in leucocyte related to immune system, and remained stable during the rest of testing time. This may suggest that FPP can regulate the functions of immune system and anti-oxidant action.
◆Reference Review Article
1). Applications and bioefficacy of the functional food supplement fermented papaya preparation.
OI. Aruoma, Y. Hayashi, F. Marotta, P. Mantello, E. Rachmilewitz, L. Montagnier
Toxicology. 2010 Nov 28;278(1):6-16. Epub 2010 Sep 24.
Fermented papaya preparation (FPP) (a product of yeast fermentation of Carica papaya Linn) is a food supplement. Studies in chronic and degenerative disease conditions (such as thalassemia, cirrhosis, diabetes and aging) and performance sports show that FPP favorably modulates immunological, hematological, inflammatory, vascular and oxidative stress damage parameters. Neuroprotective potential evaluated in an Alzheimer's disease cell model showed that the toxicity of the β-amyloid can be significantly modulated by FPP. Oxidative stress trigger apoptotic pathways such as the c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38-mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) are preferentially activated by pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress resulting in cell differentiation and apoptosis. FPP modulated the H₂O₂-induced ERK, Akt and p38 activation with the reduction of p38 phosphorylation induced by H₂O₂. FPP reduces the extent of the H₂O₂-induced DNA damage, an outcome corroborated by similar effects obtained in the benzo[a]pyrene treated cells. No genotoxic effect was observed in experiments with FPP exposed to HepG2 cells nor was FPP toxic to the PC12 cells. Oxidative stress-induced cell damage and inflammation are implicated in a variety of cancers, diabetes, arthritis, cardiovascular dysfunctions, neurodegenerative disorders (such as stroke, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease), exercise physiology (including performance sports) and aging. These conditions could potentially benefit from functional nutraceutical/food supplements and fermented papaya preparation) exhibiting anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunostimulatory (at the level of the mucus membrane) and induction of antioxidant enzymes.
◆Reference Book
"The intelligent way to live starving off diseases"
(original French title: Les Combats de la vie)
Author: Luc Montagnier, a board member of Osato Research Institute, 2008 Nobel laureate in Medicine
Medical supervising editor:Kuniaki Nerome
Translation:Yuko Tanaka
Published by East Press
Available at bookstores throughout Japan
- 2011.04.13
- WHAT'S NEW
