Research
REGULATING REDOX BALANCE GENE EXPRESSION IN HEALTHY INDIVIDUALS BY NUTRACEUTICALS : A PILOT STUDY
FILE2010
Marotta F(1), Koike K(2), Lorenzetti A(1), Jain S(3), Signorelli P(1), Metugriachuk Y(2), Mantello P(2), Locorotondo N(4)
We tested the effect of a fermented papaya preparation (FPP, ORI, Japan) on redox balance gene expression in 11 healthy non-smoker, teetotaller individuals subjected to a detailed dietary and lifestyle questionnaire who refrained from any multivitamin supplement or fortified food. Redox status was assessed by erythrocyte and plasma parameters together with related leukocyte mRNA (GPx, SOD, Catalase, hOGG1) before/after 6gr FPP supplementation. At 2-/4-week observation, plasma parameters remained unchanged while FPP significantly upregulated all tested gene expression (p<0.05).
On the other hand, already starting at 2-week observation, FPP brought about a significant upregulation of all gene expressions checked (fig. 1, p<0.05) which remained stable at later testing time. This data applied irrespective of GSTM-1 and h-OGG-1 genotype profile. While post-transcriptional/translation protein modifications do occur and larger and longer studies are awaited, these preliminary data suggest that a transcriptomic modification of key redox and DNA repair genes may offer further insights when attempting to interrelate "nutragenomics" to clinical phenomena.
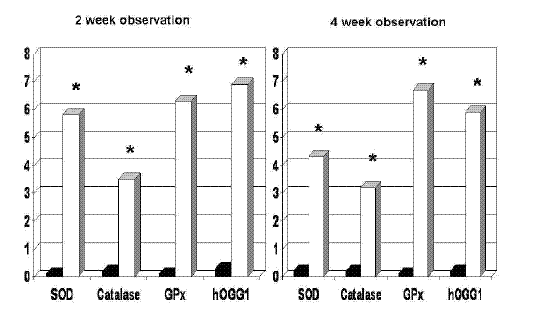
All subjects fully complied with the study protocol. At either 2 and 4 week observation, plasma level of tested redox parameter did not change after FPP supplementation, besides a non-significant decrease of MDA. On the other hand, already starting at 2-week observation, FPP brought about a significant upregulation of all gene expressions checked (p<0.05) which remained stable at later testing time. This data applied irrespective of GSTM-1 and h-OGG-1 genotype profile. No relation correlation appeared between erythrocyte level of redox parameters or plasma MDA and related gene expression or genotype profile.
(1)ReGenera Research Group, Milano, Italy; (2)ORI Bioscience Laboratory, Gifu, Japan; (3)Dept of Nutrition, Illinois University, Urbana, USA; (4)Gruppo Locorotondo laboratories, Palermo, Italy
Rejuvenation Research Volume13, Number 2 (2010)
List of the related papers
Year
Name of Papers
2010
2007
2006
