Osato Research Institute supports Aston Martin Racing as official partner
Since the Aston Martin came back to Le Mans in 2005, the Osato Research Institute has been supporting drivers' health of Aston Martin Racing with Immun'Age (FPP - Fermented papaya preparation) as their official partner.
The purpose is to prevent drivers' oxidative stress during the race and decrease DNA damage. In order to prove it scientifically, analysis of blood samples of the drivers were necessary, though it is impossible to get them during the race. However, it has become possible through collaboration with the Grenoble University to obtain results from analysis of urine sample. In 2007, we conducted a research with 009 DBR9 drivers during Le Mans 24-hours race. The result was Aston Martin's first victory since they triumphed overall in 1959 and we gained a data to prove DNA damage decrease of two drivers - David Brabham and Darren Turner - who took FPP.
At Le Mans 2008, all the members of 009 DBR team including drivers and pit crews took FPP. And then, let me be allowed to say that the drivers, car, and all the team members not only formed a firm unity but also accomplished a great achievement of the two consecutive years wins.
Yuki HAYASHI
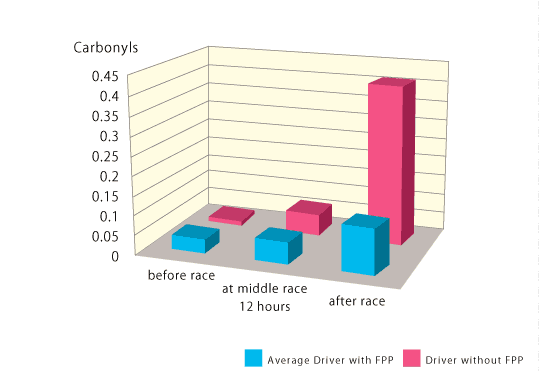
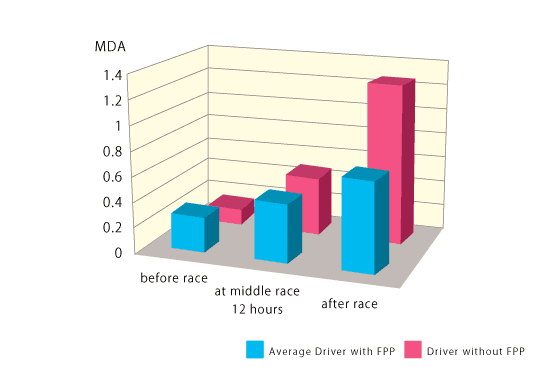
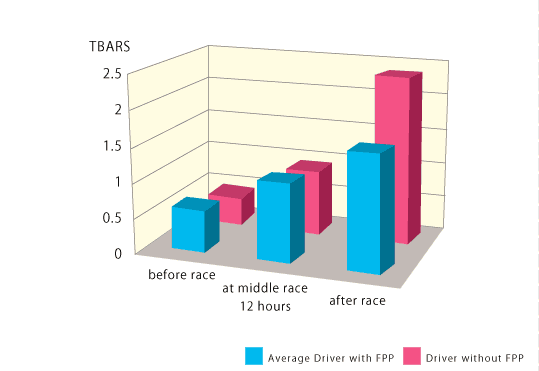
At the three all oxidative stress markers, The results of the two supplemented drivers shows that FPP significantly protects them against increase of oxidative stress comparatively of the non supplemented driver.
Markers of oxidative stress
MDA
Malondialdehyde(MDA) is the end-product of lipid peroxidation, which is a process where reactive oxygen species degrade polyunsaturated lipids. This compound is a reactive aldehyde and is one of the many reactive electrophile species that cause toxic stress in cells and form advanced glycation endproducts. The production of this aldehyde is used as a biomarker to measure the level of oxidative stress in an organism.
TBARS
Thiobarbiturate reactive substances (TBARS) are the low-molecular-weight end products, whose main component is malondialdehyde, that are formed during the decomposition of lipid peroxidation products. These compounds react with thiobarbituric acid to form a fluorescent red adduct which can be measured spectrometically. The plasma or urine concentration of the thiobarbiturate reactive substances (TBARS) is used as an index of lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress./p>
Taux carbonyls
Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS and RNS) are formed during normal metabolism and in higher fluxes under pathological conditions. They cause cellular damage, an important part of which is the oxidation of amino acid residues on proteins, forming protein carbonyls. Protein carbonyl content (PCC) is the most widely used marker of oxidative modification of proteins. Using PCC as a marker, it could be demonstrated that oxidative damage to proteins correlates well with aging and the severity of some diseases. A critical evaluation of PCC and other markers of protein oxidation is presented, together with examples of protein oxidation in diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases, and aging.
"Human studies related to protein oxidation: protein carbonyl content as a marker of damage"
M (Mordechai) Chevion, E Berenshtein, ER Stadtman Free Radic Res (2000) 33: S99-108.

